- Director Research
- About Department
- Joint Directors
- Research Centres
- Research Highlights
- Crop Varieties
- Achievements
- Developed Technologies
- New Technologies
- Patents
- Knowledge Resources

-
Dr. S.K. Verma Director Research G.B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology Pantnagar – 263145, Uttarakhand, India Contacts +91-5944-233363 (O) desgbpuat[at]gmail[dot]com
The Genesis
The Directorate of Experiment Station was established with the inception of the University in the year 1960 and has the following mandate:
- Coordination of all research activities, fundamental and applied in different disciplines of science and technology.
- Development, evaluation, processing, monitoring and budgeting of research projects and programmes in the University.
- Administration, management and monitoring of research centres located at the main campus and outside in four agro-climatic zones covering all districts of Uttarakhand.
- Production of nucleus, breeder, foundation and certified seeds of different crop plants and planting material of crops and plants viz., cereals, pulses, oil seeds, sugarcane, forage crops, green manure crops, vegetables, sub-tropical and temperate fruit crops, ornamental plants, medicinal and aromatic plants, agro-forestry plants, mushroom and fisheries.
- Production and monitoring of bio-control agents, bio-fertilizers and vermi-compost.
- Monitoring the production of livestock and poultry and other research aspects related to production and health of animals and poultry. Development of suitable implements for agriculture in both hills and plains.
- Publication of ‘International Journal of Basic and Applied Agricultural Research’ as well as research reports, manuals and highlights etc., and
- Processing of research papers for publication in national/international journals.
Research Organization and Administration
The research organization of the University is governed by a ‘Research Advisory Committee’ (RAC). The Vice-Chancellor is the Chairman and Director, Experiment Station is the Member Secretary of the committee. The Deans of different colleges, Directors of various directorates in the University, Programme Coordinators and Comptroller are the members. Besides, Directors of Directorate of Agriculture, Horticulture and Fisheries of Government of Uttarakhand as well as Heads of State departments like soil conservation, sericulture, animal husbandry, forestry, marketing, medicinal and aromatic plants are also the members. Some progressive farmers also represent the RAC as member. The RAC as facilitators identify and orient research to address problems of farming community.
The Directorate of Experiment Station has a set-up which distinctly looks after technical, financial and administrative management as well as the management of on-campus and off-campus research centres. The Director Experiment Station is the head of the set-up and is assisted by Joint Directors from disciplines of Agriculture, Veterinary and Engineering as well as by Joint Director Research for Administration and Monitoring. The on- and off- campus research stations have Joint Directors/ Associate Directors/ Officer-in-charges for planning and execution of mandate of these centres and a Joint Director at Head quarters monitors these activities. The Comptroller in association with a Deputy Comptroller and other accounts officials takes care of financial management of the directorate.
| Sl. No. | Name & Designation | Name of Department | Email Id |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dr. Subhash Chandra JDR-NARS (National Agriculture Research System) |
Directorate of Research | schandra_1961@yahoo.com | |
| Dr. K.P. Singh JDR-FRTP (Farmers Research & Training Programme) |
Directorate of Research | kpsingh.gbpuat@gmail.com | |
| Dr. P.K. Singh JDR-IC (Institutional Collaboration) |
Directorate of Research | singhpk67@gmail.com singhpk67@rediffmail.com |
|
| Dr. Manjul Kandpal, JDR- Administration |
Directorate of Research | manjulkandpal@yahoo.com | |
| Dr. Anil Kumar JDR-SPR (State Policy Research) |
Directorate of Research | yaduanil@gmail.com | |
| Dr. M.S. Negi JDR-IPM (Intellectual Property Management) |
Directorate of Research | mahendrasingh_2005@rediffmail.com | |
| Dr. S.B. Bhardwaj Associate Director Admin |
Directorate of Research | sbb20aug@yahoo.com desgbpuatpmc@gmail.com |
|
| Dr. Ajay Srivastava Asstt. Director, Research |
Directorate of Research | drajaysrivastava@gmail.com |
Directorate of Research (On & Off Campus Research Centres)
On Campus Research Centres
Off-Campus Research Centers
On Campus Research Centres)
| Name of the Centre | Officer Incharge | Year of Establishment | Area (in hectares) |
Mailing Address | Contact no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Norman E. Borlaug Crop Research Centre | Dr. S.K. Verma Joint Director |
1962 | 139.61 | PO - Pantnagar, Distt. U.S. Nagar, Uttarakhand-263145 | +91-9411324848 |
| Breeder Seed Production Centre | Dr. A.S. Jeena Joint Director |
1992 | 284.08 | PO - Pantnagar, Distt. U.S. Nagar, Uttarakhand-263145 | +91-7817005207 |
| Vegetable Research Centre | Dr. Lalit Bhatt Officer In-charge |
1999 | 40.00 | PO - Pantnagar, Distt. U.S. Nagar, Uttarakhand-263145 | +91-7500241512, +91-9412986485 |
| Pantnagar Centre of Plant Genetic Resources | Dr. J.P. Jaiswal Nodal Officer |
1999 | 0.60 | PO - Pantnagar, Distt. U.S. Nagar, Uttarakhand-263145 | +91-9411159751 |
| Medicinal and Aromatic Plants Research and Development Centre | Dr. V.P. Singh Joint Director |
2003 | 40.00 | PO - Pantnagar, Distt. U.S. Nagar, Uttarakhand-263145 | +91-9536102111 |
| Agroforestry Research Centre | Dr. Ashutosh Dubey Associate Director |
2003 | 57.00 | PO - Pantnagar, Distt U.S. Nagar, Uttarakhand-263 145 | +91-9012744161 |
| Model Floriculture Centre | Dr. V.K. Rao Joint Director |
2004 | 12.00 | PO - Pantnagar, Distt U.S. Nagar, Uttarakhand-263145 | +91-05944-233055, +91-7500241434 |
| Horticulture Research Centre | Dr. A.K. Singh Joint Director |
1968 | 181.00 | PO - Pantnagar, Distt U.S. Nagar, Uttarakhand-263145 | 7900280111 |
| Mushroom Research and Training Centre | Dr. S.K. Mishra Joint Director |
2003 | 1.00 | PO - Pantnagar, Distt U.S. Nagar, Uttarakhand-263145 | +91-8475008884 |
| Model Bee Research & Training Centre | Dr. Pramod Mall Joint Director |
2013 | 32.40 | PO - Pantnagar, Distt U.S. Nagar, Uttarakhand-263145 | +91-9456345516 |
Off Campus Research Centres
| Name of the Centre | Officer Incharge | Year of Establishment | Area (in hectares) |
Mailing Address | Contact no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sugarcane Research Centre, Kashipur | Dr. Sanjay Kumar, Officer In-charge | 2002 | 83.60 | Sugarcane Research Centre, G.B.P.U.A.T., Bazpur Road, Kashipur-244713, Distt. - U.S. Nagar, Uttarakhand | +91-7500241511 |
| Agriculture Research Centre, Majehra (Nainital) | Dr. Anjuli Agrawal, Officer In-charge | 1973 | 8.19 | P.O. Garampani, Distt. Nainital, Uttarakhand | +91-7500241431 |
| Research & Training Centre, Pauri | Er. Umesh Kumar Saxena, Officer In-charge | 1973 | 0.30 | P.O. Pauri, Distt. Pauri Garhwal, Uttarakhand | +91-9917747271 |
| Pantnagar Rural Bioresource Centre, Bhagwanpur | Dr. Dinesh Kumar Singh, Officer In-charge | 2006 | 10.93 | Khanna Farm, Bhawanpur, Rudrapur (U.S.Nagar) | +91-9410187299 |
| Research Station Sui-Lohaghat | Dr. Amresh Sirohi, Officer In-charge | 1994 | 12.00 | P.O. Lohaghat, Distt. Champawat, Uttarakhand | +91-9412088082 |
| Jyotiram Kandpal Hill River Valley Integrated Agricultural Research and Extension Centre | Dr. V.P. Singh, Officer In-charge | 2011 | 1.74 | Kahergaon, Siyaldeh, Almora | +91-9411516990 |
| Research Centre, Dhakrani | Dr. A.K. Sharma, Officer In-charge | 2004 | 23.35 | P.O. Dhakrani, Distt. Dehradun – 248142 | +91-8475002277 |
| Research Centre, Gaina-Anchauli | Dr. Guari Shankar Bisht, Officer In-charge | 2004 | 17.00 | KVK Gaina, P.O. Anchauli Distt. Pithoragharh- 262530 | +91-9412344527 |
RESEARCH PROJECTS IN OPERATION
At present 134 research projects with financial outlay of Rs 32.25 crores are in operation at different colleges and on- and off- research centres of the University funded by ICAR, Central and State Government, International Agencies.
Ongoing Research Projects 2022: Click Here
SALIENT RESEARCH ACHIEVEMENTS
The University has made significant achievements on agricultural research front and has developed a number of technologies for adoption by farmers and other end users. Some of the achievements are given below:
University has so far released 280 improved varieties of cereals, pulses, oilseeds, fodder crops, sugarcane, green manure crops, vegetables crops of Kharif and Rabi seasons, fruits crops and plants species, agroforestry and flowering plants. The crop varieties have great potential and contributed significantly to enhance the productivity in the state and the country. The University has focused research efforts to meet specific requirements of Uttarakhand and more than 100 varieties of different crops have been released for cultivation in different parts of the state under various cropping systems.


























- The University touched the new heights by bagging the Sardar Patel Outstanding Agricultural Institutional Award (2005) of Indian Council of Agricultural Research.
- During the Union Budget Speech 2007-08 the Government of India recognized the University as “Institution of Excellence” and allocated a special grant of Rs 50 crores.
- The University has been awarded with the “Service to Humanity Award” for outstanding contributions to the humanity.
- The University is playing a vital role to make Uttarakhand as focal point of organic farming and a project is being implemented in 24 villages where local varieties are being identified for cultivation under organic mode. For the benefits of the farmers, a package of practices for organic farming of rice, chickpea, frenchbean and rajma have been developed.
- The University has initiated research on jatropha and has entered into MoU with M/S Hindustan Petroleum Corporation for production of bio-diesel.
- The University in association with M/S Armaco Consultant Pvt. Ltd. has launched a programme to promote anti-malarial drugs from a medicinal plant called Artimisia.
- The University also achieved a record production of carp seed and stocked about 40 lacs quality seed in the reservoirs of Uttarakhand. The seed was also supplied and sold to the farmers of Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and Nepal.
- Research on Alternative Fuel: The nursery and plantation of 1.10 lakh plants of Jatropha curcas was taken up the University farm and outstations viz., Majhera, Lohaghat and Kashipur. The nursery raising techniques through organic means has been standardized and pruning schedule has been developed. The chemical analysis for oil content from the collection at Garhwal region revealed high oil content (40%). The accessions with high oil content will be selected and distributed among the farmers for cultivation.
- Molecular biology group at Pantnagar has shown that Alternaria blight is mediated through host selected toxin(s). Phytohormone has been shown to antagonize the toxic effect.
- In-vitro microtuber seed development has been standardized as an effective and cheaper method for potato seed production. The process of microtuber development has been made economically viable and by using cheaper and easily available ingredients.
- A strong IPM programme was developed both at Pantnagar and Hill campus, Ranichauri to promote the use of biocontrol agents and other non-chemical methods of disease and pest management. The products developed during the programme: Pant Biocontrol Agent-1 (Trichoderma harzianum, TH), Pant Biocontrol Agent-2 (Pseudomonas fluorescens, PsF), Pant Biocontrol Agent-3 (TH+PsF), Pantgramma I (Trichogramma japonicum), Pantgramma II (Trichogramma chilonis), Pantgramma III (Trichogramma poliae; new species isolated from eggs of Populus deltoides).
- The extraction of natural dyes mordanting, dyeing, printing on various kinds of fabrics using plant source like Berbis vulgaris, Jatropha integerimma, Juglan regia, Hamelia patens, Butea monosperma etc have been standardized. Tea leaves, Amla, Bahera, lemon etc have been used as moderant (eco-friendly). Techniques have been developed for dyeing and printing on garments like cotton, silk and wool.
- Ovum pick technology for obtaining progenies from infertile animals of high pedigree for genetic improvement has been perfected.
Organic Farming Technologies
Organic production technology has been developed for most of the crops which are being grown under Tarai as well as hilly areas. Under Tarai conditions organic package of practices have been developed for Basmati rice based cropping systems. Basmati rice grain yield during five years of experimentation showed a increasing trend though slight increase in initial 3 year and a drastic increase in fourth and fifth year in 100% organic mode (52.0% more over initial) and this observed cumulative yields of basmati rice over years under organic mode of nutrient management may be attributed to the build up of organic matter, accumulation of nutrients over years and improvement in physico-chemical properties of soil.
Organic mode of cultivation recorded on an average highest net return after three years of conversion period and up to three years it was highest in inorganic mode of cultivation. Among the cropping systems, highest net return and B: C ratio was recorded with basmati rice-vegetable pea system followed by basmati rice- lentil system in all the modes of nutrient management during all the years.
Propagation of Haldu (Adina cordifolia)
Propagation technology reported for the first time on rooting in Adina cordifolia using macro propagation technique using mono nodal leafy softwood cuttings prepared from epicormic shoots using 6000 ppm IBA. The technology is helpful in cloning, domestication and mass multiplication of the species. This technique is useful in overcoming the problem of poor seed germination in the species which hinders the nursery production.
Propagation techniques for multiplication of bamboos
Propagation techniques for multiplication of bamboos in sand without use of mist chamber has been developed which can increase success for bamboo rooting and can produce more number of roots. In addition macroproliferation technique with use of fertilizer was standardized which can give higher number of plants as compared to standard technique.

Root training in litchi
Air layering is only means to multiply litchi plants. Air layers in litchi produce thick and brittle roots which results in heavy mortality of rooted plants in nursery and field as well. However, after separation from mother plants, air layers were subjected to root training by planting in root trainers which produced more number of thinner lateral roots and resultantly enhanced survival of air layered plant in the field.

Pant zero-till ferti-seed drill (Tractor drawn)
This drill reduces sowing time by 10-15 days and saves Rs. 1,500-2,000 per hectare. The Pant Zero-till ferti-seed drill (ZT drill) is a tractor mounted drill (9,11and 13 tynes) used for sowing wheat in rice- wheat crop rotation, over a dozen agricultural machinery manufactures are manufacturing this drill who have sold about 4,000 drills so far.
Pant zero-till ferti-seed drill (Animal Drawn)
Pant animal drawn zero till seed drill having single, two and three rows had been developed and popularized. The one and two seed drill is suitable for use in hills while three row zero-till seed drill is recommended to be used in plain region. Zero till ferti-seed drill is suitable for sowing wheat, pulses and oil crops. The weight of drill is 30 kg and can be shifted easily from one terrace to another. The area sown is 0.15-0.25 hectare/day approximately and two row drill costs Rs. 2500/-.

Pant hill yoke
The Pant hill yoke suitable for hill bullocks has been developed and fabricated. The animals feel comfortable while using this yoke due to large neck contact area compared to local yoke. The cost of Pant hill yoke is Rs.280/-per unit, weight 3 kg approximately and is made of Tun wood (light weight hill wood having very good strength). An increase in pulling capacity of 9-10% has been observed enabling farmers to use large size implements/tools even under adverse field conditions. More than 400 no. of hill yokes have been marketed by the department in hill region.
Multi-fruit grader
A multi-fruit grader suitable for grading spherical fruits has been developed. The grading principle is based on varying weights of fruits. It is most suited for grading oranges. The capacity of the grader is 250kg/hour.
Pant dal mill
A new technology of miling has been developed in which pigeon pea grains are treated with edible sodium solution for loosening the husk. The use of bicarbonate treatment increases digestibility and reduces flatulence. This technology is ready for delivering to dal mill owners. There is an increase in dal recovery by 6 to 8% as compared to conventional methods.
Quality Litchi Production under Drip fertigation
Study conducted on response of micro irrigation and fertigation in grownup litchi orchard reveals that average marketable fruit yield (176.22 kg/tree) over the years was significantly higher (56%) in treatment under bubbler irrigation at 100% of estimated irrigation water requirement + 125% of recommended dose of fertilizer (N:P2O5:K2O:: 1500:750:750 g) as compared to conventional practices (112.94 kg/tree). Micro irrigation and fertigation also increases the fruit length (8.5%) and fruit width (6.4%), fruit weight (19.9%) along with significant reduction in fruit cracking (69.9%).

Development of vaccine
A potent cell culture vaccine against fowl pox virus in poultry was developed. Fowl pox virus was first attenuated in cell culture including CEF, CEL, CEK and also in non avian origin BHK-21 cell line. The attenuated virus was tested for its disease producing ability and thereafter its disease protection capability. However, further field trials are necessary before its commercial use.
Super-ovulation
Super-ovulation was induced in New Zealand white rabbits (daily injection of 50 I.U. of PMSG for 3 consecutive days) and goats (with 750 I.U. PMSG given twice on subsequent days followed by 1000 IU hCG at estrus/ mating). Embryos were collected 100 hrs after mating from uterus and transferred to uterus of estrus-synchronized rabbit and goats by surgical methods resulting into embryo survival rate of 67.5 and 63.5 per cent, respectively. Freezing of 4-cell goat embryos revealed a good cryoprotection effect with 2.0 M DMSO in goat.
In buffaloes, a superovulatory response of 2.66 ovulations was recorded with 2000 IU PMSG. In cattle, superovulation was successfully induced with 50 mg FSH-P in crossbred cows and with 60 mg FSH-P in Sahiwal cows. A positive correlation was observed between blood progesterone level at the initiation of Gonadotrophin treatment and ovulation rate. The mean recovery rates of embryo, transferable embryo and good quality embryo were 5.25, 3.00 and 1.8 per flushing, respectively. The mean pregnancy rate on transfer of frozen and fresh embryos was 23.8% and 36.4%, respectively, while a pregnancy rate of 76.9 per cent was recorded on transfer of fresh embryos of good quality. The pregnancy rate was significantly improved if recipient cows were injected with 10 mg Buserelin acetate on day 5 post-embryo transfer. Seven healthy calves were produced through embryo transfer from one donor cow in one year.
In-vitro maturation and In-vitro fertilization
The technique of in vitro oocyte maturation (IVM), sperm capacitation, in-vitro fertilization (IVF), embryo culture and cryopreservation of oocytes and embryo have been standardized. Oviductal cell co-culture is beneficial for embryo development up to 8-cell stage beyond that its beneficial effect is lost. Technique has been established to cryopreserve buffalo oocytes by vitrification. Timings of nuclear maturation in buffalo oocytes during in-vitro maturation and fertilization have been determined. Technique of in-vitro capacitation of buffalo spermatozoa has been developed. IVM and IVF have been successfully achieved with frozen thawed buffalo oocytes.
Embryo freezing
The study on embryo freezing indicated that the 4-cell goat embryos could be successfully frozen in Cassau mini straws in the presence of 2.0 M DMSO at cooling rate of 1.00C/ min from 00C to -500C and 20C/ min from -510C to -800C before transfer to liquid nitrogen.


Pant Fertilizer Band Placement Cum Earthing Up Machine

Pant Axial Flow Multi-Crop Thresher For Hilly Region
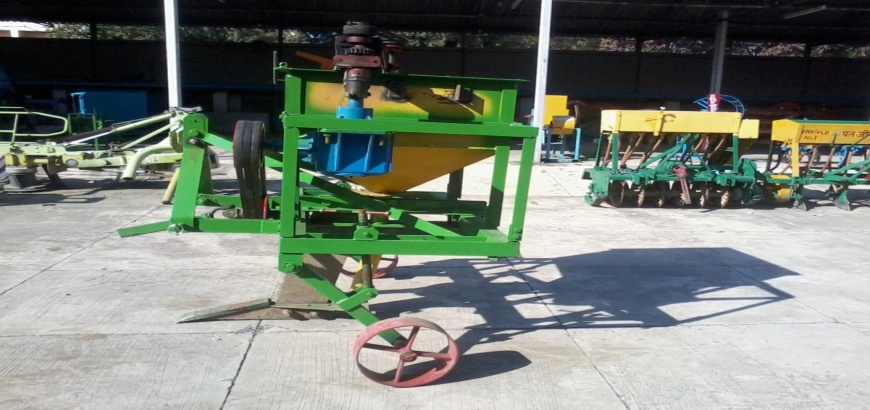

Pant Subsoiler-cum-Vermicompost and Soil Amendments Applicator
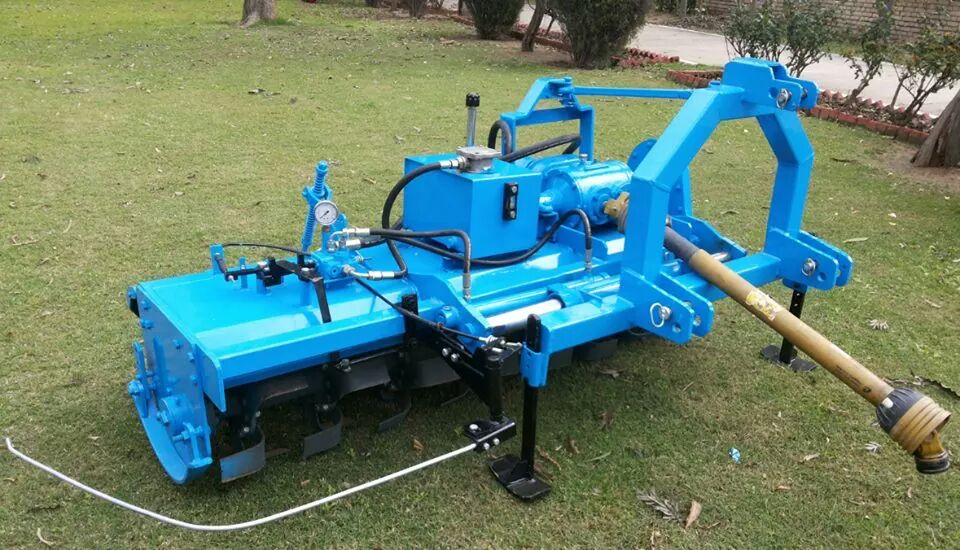

Offset Rotavator

Offset Rotavator

Pant Integrated malting unit

Finger millet dehuller-cum-pearler

Improved Pant malting unit
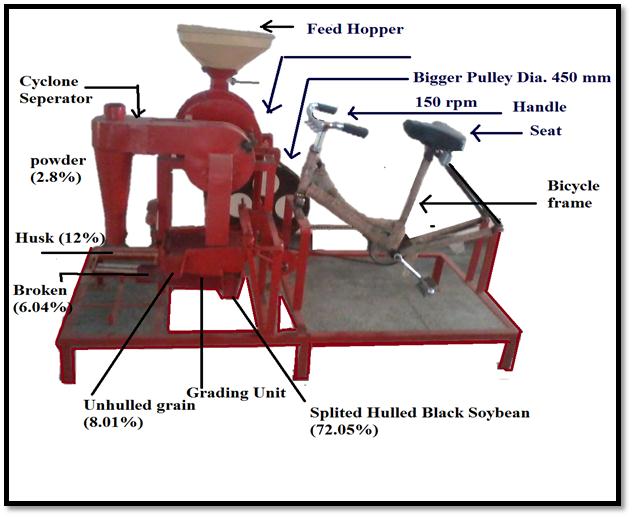
Pedal operated dehuller for black soybean

Integrated Potato peeler cum slicer

PID control Solar dryer
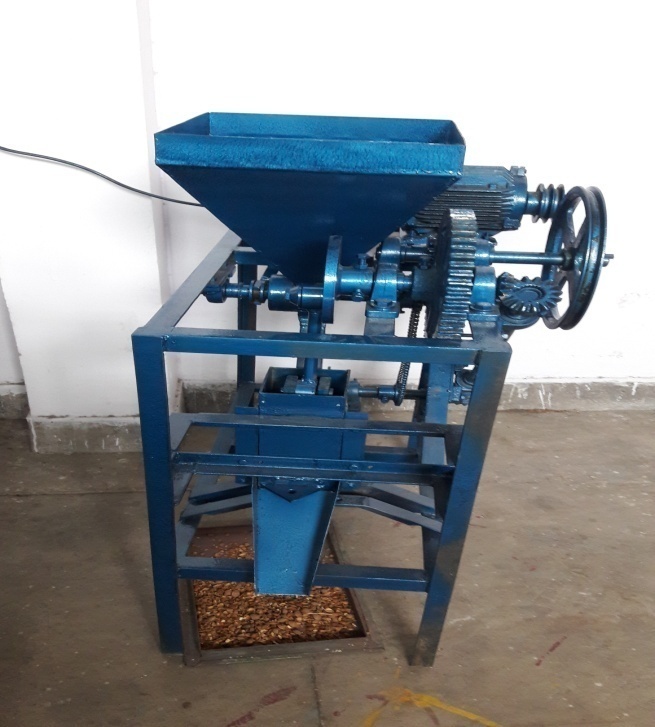

Pant apricot decorticator

Low Level Chair
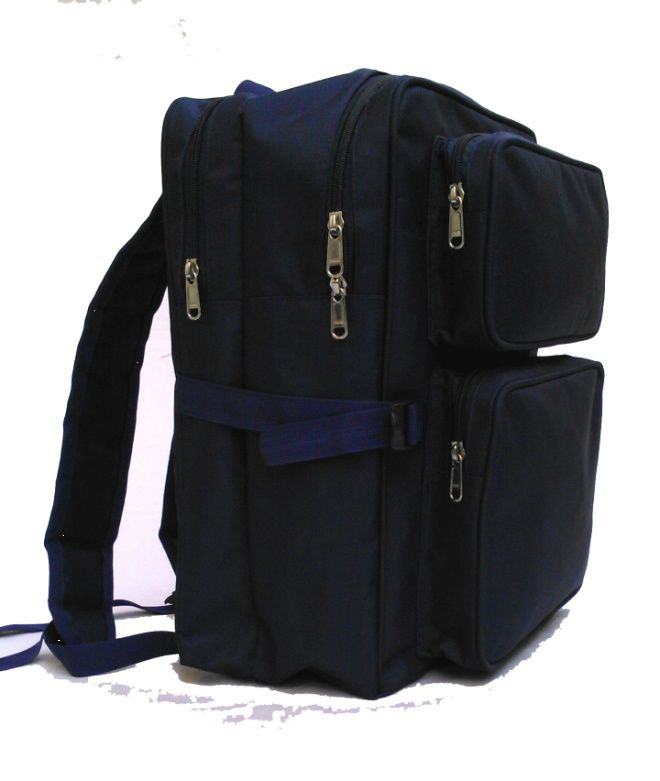

Ergonomically designed school bag

Pantloading ramp

Grain Picker
| S.No. | Invention Title | Name of College | Patent Number | Date of Grant |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A Process for Preparing Salmonella Vaccine (Non-Living) | Veterinary & Animal Science | 191823 | 30-07-2004 | |
| A Process for Preparing Salmonella Vaccine | Veterinary & Animal Science | 189049 (India) | 29-08-2003 | |
| A Process For The Preparationn Of Sweetened Puffed Wheat Snacks Rekha Balodi & Dr. J. Kumar |
Agriculture | 238683 | 17-02-2010 | |
| A Process For The Preparation Of Spiced Wheat Namkeen Dr. Y.K. Jha & V. Srivastava |
Agriculture | 239896 | 07-04-2010 | |
| A Novel Bio Fuel For Use As A Source Of Energy For C.I. Engines Dr. V.K. Gupta, J. Kandpal, Gaurav Kumar, V.K. Agrawal |
Technology | 246028 | 09-02-2011 | |
| A Process For Producing Freeze Texturized Mushrooms And Their Spents Dr. Nirankar Nath, Narendra Shah |
Agriculture | 245273 | 11-01-2011 | |
| Plant Animal Drawn Zero-Till Ferti-Seed Drill Jayant Singh & M.P. Singh |
Technology | 242551 | 01-09-2010 | |
| A Process For The Preparation Of Processed Cheese Spread Dr. Y.K. Jha & Mr. Sudhir Kumar |
Home Science | 245014 | 28-12-2010 | |
| A Process For The Prepration Of A Plant Growth Promotory Bioagent Dr. Anil Kumar Sharma & Dr. Rashmi Srivastava |
Basic Science & Humanities | 237946 | 14-01-2010 | |
| A Fule For Compression Ignition Engine Jayant Singh, P.K. Sarkar & T.K. Bhattacharya |
Technology | 253920 | 03-09-2012 | |
| A Process For Mass Multiplication Of Pseudomonas Fluorescens On Cow Dung Dr. U.S. Singh & Nazam waris Jaide |
Agriculture | 242067 | 09-8-2010 | |
| Novel Plant Dye Dr. Manisha Gahlot |
Home Science | 249691 | 03-11-2011 | |
| A Method Of Producing A Reinforced Epoxy Resin Nanocomposite Dr. M.G.H. Zaidi |
Basic Science Humanities | 256138 | 07-5-2013 | |
| Process for the Preparation of Talc Based Formulation for LDPE-Degrading Bacterial Consortia Dr. Reeta Goel, Ms. Aditi Sah, Ms. Harshita Negi & Mr. Anil Kapri |
Basic Science Humanities | US 9,057,058 B2 (US Patent No.) | 16-6-2015 | |
| Vaccine for protection of poultry against salmonellosis and a process for preparing the same Dr. V.D. Sharma, Mr. Subodh Kumar, Mr. Shri Krishna Garg, Mr. Ram Sagar Mishra, Mr. Tarani Kanta Barman |
Veterinary & Animal Science | 189049-96 (India) US 6,605,285 B2 (US Patent No.) |
12-08-2003 | |
| Bacterial Consortia for low-density polyethylene biodegradation Dr. Reeta Goel |
Basic Science Humanities | 277356 | 18-11-2016 | |
| Formulation of Bacterial Consortium for Degradation of High-Density Dr. Reeta Goel |
Basic Science Humanities | 278739 | 29-12-2016 | |
| Immunoligical Marker to Assess the Pathogenicity Levels of T.India Fungal Isolates Dr. Anil Kumar |
Basic Science Humanities | 279419 | 20-1-2017 | |
| A Novel Hybrid Renewable Fuel Blends Of Karanja Oil Ethanol For Compression Ignition Engine Dr. Jayant Singh |
Technology | 285187 | 14-7-2017 | |
| Decontaminated formulation for farm-gate vegetables and process for preparing the same Dr. Anjana Srivastava |
Basic Science Humanities | 300279 | 24-8-2018 | |
| Process for the preparation of talk based formulation for LDPE-Degrading Bacterial Consortia Dr. Reeta Goel, Ms. Aditi Sah, Ms. Harshita Negi & Mr. Anil Kapri |
Basic Science Humanities | 298158 | 27-6-2018 | |
| Paneer with extended shelf-life and process for preparing of the same Reeta, Anil Kumar, Gurmukh Singh, Krishna Rao Babu Kumbhar |
Agriculture & Technology | 317802 | 07-8-2019 | |
| A subsoiler-cum-differential rate fertilizer applicator Dr. T.C. Thakur, Er. S. Rababi, Er. S. Mandal and Mr. S.P. Dhyani |
Technology | 315451 | 03-07-2019 | |
| A method of preparing antibacterial nanocomposites Dr. M.G. H. Zaidi, Dr. Reeta Goel, Tithi Agarwal & Harshita Negi |
Basic Science Humanities | 307178 | 12-02-2019 | |
| PCR based detection and diagnostic kit and processes thereof for identification of Blast Disease and its pathogen Rekha Balodi & Dr. J. Kumar |
Agriculture | 339166 | 23-06-2020 |




