About Us
Agricultural Engineering is one of the constituent departments of college of Technology with Govind Ballabh Pant University of Agriculture and Technology, Pantnagar. After the establishment of university in the year 1960 on Land Grant Pattern of USA, the college of Agricultural Engineering came into existence in the year 1962. Later on in the year 1966, College of Technology was established which led to the merger of College of Agricultural Engineering into it. The Agricultural Engineering became one of the constituent departments of college of Technology. Further in the year 1984, the department of Agricultural Engineering was reconstituted into four departments namely Farm Machinery and Power Engineering, Irrigation & Drainage Engineering, Soil & Water Conservation Engineering and Post Harvest Process & Food Engineering. All the four departments are jointly responsible for teaching and awarding the degree of Agricultural Engineering at under graduate (B. Tech.) level, where as Post Graduate degrees (M. Tech and Ph. D.) are awarded separately by all the four respective departments.
Vision: The vision of the department is to become a nationally recognized leader in the field of Agricultural Engineering Education, Research, and Technology Transfer.
Mission: Mission of the department is as under:
Program Educational Objectives (PEOs) The PEOs of the department of Agricultural Engineering are given as under:
- To provide students with a comprehensive knowledge in mathematical, scientific and agricultural engineering fundamentals to solve the engineering and farmers related problems and also to pursue higher studies.
- To provide students experience for planning as well as conducting experiments/ projects in modern engineering laboratories including farmers’ friendly technologies and computer based simulation experiments, integrating the significance of experimental data and properly reporting the results.
- To develop ability of the students to analyze data and technical concepts for application to product design and/or solving real field problems.
- To make the students familiar with latest and contemporary professional knowledge in the field of agricultural engineering including managerial skills and ethics required for emerging technologies, global economy and also to foster other skills required for grooming them into good professionals.
- To prepare the students for their successful career in industry/scientific institutions/ technology transfer organizations and also to meet the challenges at national and international levels.
The various departments under Agricultural Engineeering
Student Intake and Attrition
| Degree Programmes | Actual Student Admitted | Attrition (%) | SSR Page | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016-17 | 2017-18 | 2018-19 | 2019-20 | 2020-21 | 2016-17 | 2017-18 | 2018-19 | 2019-20 | 2020-21 | ||
| B.Tech. | 49 | 47 | 51 | 47 | 64 | 2.04 | 12.76 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| Post Harvest Process & Food Engineering | |||||||||||
| M.Tech. | 06 | 05 | 06 | 05 | 05 | Nil | Nil | 25 | 25 | Nil | 12 |
| Ph.D. | 04 | 03 | 01 | 03 | Nil | 25 | Nil | 100 | Nil | Nil | 34 |
| Farm Machinery & Power Engineering | |||||||||||
| M.Tech. | 08 | 13 | 06 | 08 | 11 | Nil | Nil | 33 | 25 | 55 | 21 |
| Ph.D. | 03 | 04 | 01 | 03 | 05 | Nil | 25 | Nil | Nil | Nil | 39 |
| Irrigation & Drainage Engineering | |||||||||||
| M.Tech. | 07 | 12 | 06 | 08 | 11 | 28.57 | 8.33 | 16.67 | Nil | 9.09 | 29 |
| Ph.D. | - | - | 01 | - | 01 | - | - | Nil | - | Nil | 48 |
| Soil & Water Conservation Engineering | |||||||||||
| M.Tech. | 09 | 09 | 10 | 09 | 10 | Nil | Nil | Nil | Nil | Nil | 25 |
| Ph.D. | 05 | 05 | 05 | 03 | 04 | Nil | Nil | 20 | 33 | Nil | 43 |
Course curriculum: In order to get degree in B.Tech. Agricultural Engineering, a student has to study the following courses.
| Course Code | Course Title | Credits | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lecture (L) | Tutorial (T) | Practical (P) | Total Hours | |||
| Basic Science courses (18 Cr hours) | ||||||
| BPM-131 | Engineering Mathematics-I | 3 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 3(3+2+0) |
| BPM-132 | Engineering Mathematics-II | 4 | 1 | - | 5 | 4(4+1+0) |
| BPC-163 | Engineering Chemistry-III | 3 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 4(3+0+3) |
| BPP-197 | Engineering Physics | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3(2+1+2) |
| BPS-218 | Probability, Statistics &Queuing Models | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2(2+1+0) |
| BPM-233 | Engineering Mathematics-III | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2(2+1+0) |
| Humanities and Social Science Courses (01 Cr hour) | ||||||
| BHS-276 | Communication Skill | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 1(0+0+3) |
| Engineering Science Courses (54 Cr hours) | ||||||
| TME-101 | Thermodynamic and Heat Engines | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 4(3+1+2) |
| TCE/TID/TPF/TMP-102 | Introduction to Environmental Engineering | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2(2+0+0) |
| TCE-131 | Solid Mechanics | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 4(3+1+2) |
| TCE-100 | Engineering Drawing | 1 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 3(1+0+2*2) |
| TIP-101 | Workshop Practice | 1 | 0 | 6 | 7 | 3(1+0+2*3) |
| TCE-337 | Analysis and Design of Structures | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 4(3+1+2) |
| TCT-100 | Introduction to Computers and Programming | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3(2+1+2) |
| TCE-211 | Surveying and Leveling | 2 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 3(2+0+3) |
| TCE-220 | Engineering Materials and Construction | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3(3+0+0) |
| TCT/TIT-242 | Database Management & Internet Applications | 1 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 2(1+0+2) |
| TME-231 | Machine Drawing | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 2(0+0+2*2) |
| TEE-260 | Electrical Circuits | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TME-240 | Theory of Machines | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TEC-262 | Applied Electronics and Instrumentation | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TCE-240 | Fluid Mechanics | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3(2+1+2) |
| TME-233 | Machine Design | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TEE-261 | Electrical Machines and Power Utilization | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TIP-201 | Manufacturing Processes | 1 | 0 | 6 | 7 | 3(1+0+2*3) |
| Program Core Courses (70 Cr hours) | ||||||
| APA/APS/APH-102 | Agriculture for Engineers | 3 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 4(3+0+2) |
| TME/TPF-202 | Refrigeration and Air Conditioning | 2 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 3(2+0+3) |
| TSW-302 | Soil Mechanics | 2 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TSW-312 | Watershed Hydrology | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TID-361 | Fluid Transport Machinery | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TMP-313 | Farm Machinery & Equipment-I | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TPF-331 | Heat and Mass Transfer | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TMP-322 | Farm Power | 2 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TMP-315 | Field Operation and Maintenance of Tractors & Farm Machinery-I | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 1(0+0+3) |
| TID-351 | Agril. Structures, Environmental Control and Rural Engineering | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TID-371 | Irrigation Engineering | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TMP/TPF-352 | CAD/CAM and Computer Graphics | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 2(0+0+4) |
| TSW-322 | Soil & Water Conservation Engineering | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TPF-311 | Engineering Properties of Biological Materials and Food Quality | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TMP-323 | Tractor Systems & Control | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TPF-380 | Dairy & Food Engineering | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TMP-316 | Field Operation and Maintenance of Tractors & Farm Machinery-II | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 1(0+0+3) |
| TID/TSW/TPF/TMP-491 | Practical Training (During Semester Break) | 0 | 0 | - | - | 30 Days |
| TMP-414 | Farm Machinery & Equipment-II | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TSW-432 | Soil & Water Conservation Structures | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TID-461 | Ground Water Hydrology & Well Engineering | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TID-481 | Drainage Engineering | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 2(1+0+2) |
| TPF 480 | Crop Process Engineering | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| TPF-488 | Drying and Storage Engineering | 3 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 4(3+0+2) |
| TMP/TPF-497 | Entrepreneurship Development | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2(2+0+0) |
| TID/TSW/TPF/TMP-410 | System Engineering | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3(3+0+0) |
| Program Elective Courses (12 Cr hours) | ||||||
| *** | Elective-I | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| *** | Elective-II | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| *** | Elective-III | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| *** | Elective-IV | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3(2+0+2) |
| Project(s)/ Dissertation (06 Cr hours) | ||||||
| TID/TSW/TPF/TMP-490(A) | Project | 0 | 0 | 6 | 6 | 2(0+0+6) |
| TID/TSW/TPF/TMP-490(B) | Project | 0 | 0 | 12 | 12 | 4(0+0+12) |
| Internships/Seminars (01 Cr hour) | ||||||
| TID/TSW/TPF/TMP-492 | Seminar | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 1(0+0+3) |
| Any other (03 Cr hours) | ||||||
| NSS-201 | NSS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2(0+0+4) |
| TWP-101 | Work Program | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 1(0+0+3) |
| Total | 99 | 11 | 139 | 249 | 165 | |
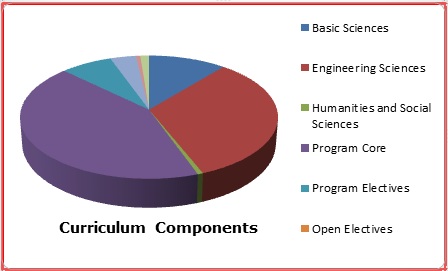
Structure of the curriculum
| Course Component | Curriculum Content (% of total number of credits of the program ) | Total number of contact hours | Total number of credits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Sciences | 10.91 | 27 | 18 |
| Engineering Sciences | 32.73 | 86 | 54 |
| Humanities and Social Sciences | 0.606 | 3 | 1 |
| Program Core | 42.42 | 96 | 70 |
| Program Electives | 7.27 | 16 | 12 |
| Open Electives | - | - | - |
| Project(s) | 3.63 | 18 | 6 |
| Internships/Seminars | 0.606 | 3 | 1 |
| Any other (Please specify): NSS and Work Program | 1.82 | - | 3 |
| Total number of Credits | 249 | 165 | |
| S.No. | Course code | Name of the course | Credit hours | Pre-requisite |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPF-451 | Element of Food Plant Design | 3(2+0+2) | TPF-331 Heat and Mass Transfer | |
| TPF-454 | Computer Applications in Post Harvest Technology | 3(2+0+2) | TCT-100 Introduction to Computers and Programming | |
| TPF-452 | Post Harvest Industry Management | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TPF-456 | Advanced Seed Processing | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TPF-477 | Food Packaging Technology | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TPF-478 | Waste and By-product Utilization | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TPF-479 | Development of Processed Products & Equipments | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TPF-484 | Food Engineering- I | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TPF-485 | Food Engineering- II | 3(2+0+2) | TPF-331 Heat and Mass Transfer | |
| TID-431 | Engineering of Bio-Systems | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TID-441 | Micro Irrigation Systems Design | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TID-452 | Rural Transport, Water Supply & Sanitation | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TID-461 | Minor Irrigation & Command Area Development | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TID-481 | Design & Maintenance of Green House | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TID/TSW-423 | Environmental Engineering | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TID/TSW-471 | Remote Sensing & GIS Applications | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TSW-415 | Watershed Planning and Management | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TSW-416 | Reservoir & Farm Pond Design | 3(2+0+2) | TSW-302 Soil Mechanics | |
| TSW-417 | Gulley & Ravine Control Structures | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TMP-423 | Tractor Design & Testing | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TMP-424 | Hydraulic Drive & Controls | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TMP-425 | Farm Power & Machinery Management | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TMP-426 | Renewable Energy Technology | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TMP-427 | Renewable Energy Sources | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TMP-428 | Human Engineering & Safety | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TMP-429 | Biomass Management for Fodder & Energy | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TMP-430 | Production Technology of Agricultural Machinery | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TMP-431 | Mechanics of Tillage and Traction | 3(2+0+2) | Nil | |
| TID/TSW/TPF / TMP-411 | Agribusiness Management and Trade | 3(2+0+2) | Nil |
Course Outcomes (course articulation matrix) The course articulation matrix has been presented as under. The correlation level 1, 2 and 3 means: 1- Slight (low), 2- Moderate (medium) and 3-Substantial (high)
| CO | Statements | PO1 | PO2 | PO3 | PO4 | PO5 | PO6 | PO7 | PO8 | PO9 | PO10 | PO11 | PO12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSW-211 Soil Mechanics | |||||||||||||
| TSW-211.1 | Compute various Engineering properties of different types of soils | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| TSW-211.2 | Apply the Knowledge of soil mechanics to design various types of structures | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | - | 3 | - | 2 | 2 |
| TSW-211.3 | Select a particular type of soil for utilization under specific conditions in nature | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| TSW-211.4 | Develop a plan for suitability of soil conservation structures at a location | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| TSW-211 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| TSW-222 Watershed Hydrology | |||||||||||||
| TSW-222.1 | Understand different components of hydrologic cycle and their importance | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 3 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| TSW-222.2 | Compute areal rainfall and runoff on a watershed scale | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | - | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| TSW-222.3 | Develop rainfall-runoff relationship for a watershed for prediction purpose | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | - | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| TSW-222.4 | Apply the knowledge on hydrology for planning watershed management projects | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| TSW-222 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | |
| TSW-371 Soil and Water Conservation Engineering | |||||||||||||
| TSW-371.1 | Understand the importance of soil & water conservation(SWC) measures for the control of soil erosion and thereby enhancing agricultural productivity | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| TSW-371.2 | Compute various design components of terraces, bunds etc. | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | - |
| TSW-371.3 | Select appropriate soil and water conservation measures at a location | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | - |
| TSW-371.4 | Apply the knowledge on engineering for design of SWC projects in watersheds | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | - |
| TSW-371 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| TSW-373 Watershed Planning and Management | |||||||||||||
| TSW-373.1 | Understand the concept of watershed as a unit of planning and development of agriculture on a watershed scale to enhance agricultural productivity | 3 | 3 | - | 2 | - | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| TSW-373.2 | Compute various parameters of hydrologic and geomorphologic characteristics of watershed | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | - | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| TSW-373.3 | Formulate the appropriate watershed management plan for implementation | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| TSW-373.4 | Apply the engineering knowledge and skill for designing various SWC projects in watersheds | 3 | 3 | - | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| TSW-373 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| TSW-382 Water Harvesting and Soil & Water Conservation Structures | |||||||||||||
| TSW-382.1 | Understand the procedures/steps for designing various water harvesting and soil conservation structures/measures | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | - | 3 | 3 | 3 | - |
| TSW-382.2 | Design various components of drop, inlet spillways, farm pond, earth embankments etc. | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | 3 | - |
| TSW-382.3 | Select appropriate water harvesting and soil conservation structures at a location | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| TSW-382.4 | Apply the knowledge on engineering for design of water harvesting and soil conservation structures in watersheds | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| TSW-382 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| TSW-428 Remote sensing & GIS applications | |||||||||||||
| TSW-428.1 | Understand the basic concepts of RS, GIS & Photogrammetry | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | - | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| TSW-428.2 | Acquaint with components & scanning techniques of RS & GIS | 3 | - | 2 | 1 | 3 | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| TSW-428.3 | Analyse digital images & classifications using various principles | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | - | - | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| TSW-428.4 | Apply the knowledge of RS & GIS techniques for natural resource management | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | - | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| TSW-428 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | |
| TMP-235 Fundamentals of Renewable Energy Sources | |||||||||||||
| TMP-235.1 | Understand the fundamentals of various Renewable Energy Sources and their applications | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | - | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| TMP-235.2 | Analyze the different approaches of solar energy collection, storage and power generation. | 2 | 3 | - | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| TMP-235.3 | Compute the power generation from solar energy and wind power systems | 2 | 3 | 3 | - | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| TMP-235.4 | Explain the construction and working principle of different Bio energy conversion systems | 3 | - | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | - | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| TMP-235 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| TMP-236 Renewable Power Sources | |||||||||||||
| TMP-236.1 | Understand the working and operating principles of different Renewable Energy Sources. | 2 | 3 | 3 | - | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | - | 3 |
| TMP-236.2 | Explain the construction, operation and working principle of biomass/MSW based power generation systems | 2 | 3 | 3 | - | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| TMP-236.3 | Design the power generation systems from solar energy, wind energy and small hydropower | 3 | 3 | 2 | - | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| TMP-236.4 | Analyze the working of different alternative energy sources | - | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| TMP-236 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| TMP-238 Farm Machinery and Equipment-I | |||||||||||||
| TMP-238.1 | Apply the knowledge of various farm machines used for farming operations and land development works including their material of constructions | 3 | 2 | 2 | - | 1 | - | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| TMP-238.2 | Calculate the forces acting on the tillage machine components, draft requirement of the various machines and economics of operating these machines | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| TMP-238.3 | Compute the size of tractor required to operate the machines | 3 | - | - | 2 | 2 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| TMP-238.4 | Select the types of machines required for specific field operations and material for their construction | 3 | 2 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| TMP-238 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| TMP-319 Tractor Systems and Control | |||||||||||||
| TMP- 319.1 | Understand construction & working of different systems of tractor clutch transmission & power flow in a tractor. | 3 | 2 | - | 2 | - | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| TMP- 319.2 | Analyze problems related clutch, gear box, traction, traction mechanics. | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| TMP- 319.3 | Relate human factors that are considered for the design of controls on tractors. | 3 | 2 | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| TMP- 319.4 | Explain construction, operation and working principles of different systems of tractor in general. | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| TMP-319 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| TMP-351 Tractor and Automotive Engines | |||||||||||||
| TMP-351.1 | Understand the working and operating principles of different systems of I.C. engines. | 3 | 2 | 2 | - | 1 | 2 | 3 | - | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| TMP- 351.2 | Indentify the different components of I.C. engines. | 2 | 1 | 1 | - | 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| TMP- 351.3 | Relate and analyze the working of different systems of engine. | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| TMP- 351.4 | Comprehend the terminologies and efficiency of I.C. engines with numerical specific to tractor engine. | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| TMP-351 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| TMP-353 Farm machinery and Equipment-II | |||||||||||||
| TMP-353.1 | Understand the principles & types of cutting mechanisms. Construction & adjustments of shear and Impact-type cutting mechanisms. | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | - | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| TMP-353.2 | Crop harvesting machinery: Mower, Reaper, windrower, reaper binder & forage harvester. Forage chopping & handling equipment. | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| TMP-353.3 | Apply threshing mechanics & various types of threshers. Straw combines & grain combines, Maize harvesting & shelling equipment, Root crop harvesting equipment -potato, Groundnut etc. | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| TMP-353.4 | Understand Cotton picking & Sugarcane harvesting equipment. Principles of fruit harvesting tools & machines. | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| TMP-353 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| TMP-376 Bio-Energy Systems: Design and Applications | |||||||||||||
| TMP-376.1 | Apply the knowledge of various design perspectives in construction and working of different bio energy systems and their applications | 3 | 3 | 3 | - | 2 | 3 | 3 | - | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| TMP-376.2 | To study biomass production techniques | - | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | - | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| TMP-376.3 | Analyze the working of different power generation system | 3 | 3 | 3 | - | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| TMP-376.4 | Understand the biodiesel and bio-hydrogen production techniques and Assessment of environmental aspect of bio energy | 3 | 2 | 3 | - | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| TMP-376 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| TMP-412 Tractor Design and Testing | |||||||||||||
| TMP-412.1 | Apply the knowledge of design procedure for various tractor systems, tractor seat and control | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| TMP-412.2 | Calculate the dimensions of various engine components, tractor seat and control | 3 | 3 | 3 | - | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| TMP-412.3 | Select the material of the engine component, appropriate number of gear selection of reduction for transmission, tyres and other important components of tractor | 3 | 2 | 3 | - | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| TMP-412.4 | Understand the importance of testing, types and testing procedure of various systems of tractors, tractor hitch hydraulic system | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| TMP-412 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| TPF-242 Engineering Properties of Agricultural Produce | |||||||||||||
| TPF-242.1 | Understand the basics of engineering properties of foods | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| TPF-242.2 | Analyse the design concepts for different food instruments / equipment | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| TPF-242.3 | Implement the engineering properties in processing machines | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| TPF-242 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| TPF -351 Post-Harvest Engg. of Cereals, Pulses & Oilseeds | |||||||||||||
| TPF-351.1 | To impart knowledge on various process technologies for cereals, pulses, oilseeds and their handling and conveying equipment | 3 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 2 |
| TPF-352.2 | To understand the working principles and selection procedure of different machineries used for processing of cereals, pulses and oilseeds | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | - |
| TPF-353.3 | To compute different unit operations in processing, storage and value addition of cereals, pulses and oilseeds | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| TPF-351.4 | To analyze the different uses of byproducts obtained from cereals, pulses and oilseed | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| TPF 351 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| TPF-355 Agricultural Structures and Environmental Control | |||||||||||||
| TPF-355.1 | To know basics of design of various agricultural structures for animals and human beings. | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| TPF-355.2 | Analyze impact of environmental, ecological and sanitation on livestock and human beings. | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| TPF-355.3 | Compute cost of agricultural structures related to animals and human beings. | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| TPF-355.4 | Apply real world problems of planning, design and execution of agricultural structures related to animals and human beings | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| TPF 355 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| TPF-362 Dairy and Food Engineering | |||||||||||||
| TPF-362.1 | Apply the knowledge of different unit operations in dairy industries | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| TPF-362.2 | Analyse the dairy plant design problems | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| TPF-362.3 | Compute the problems based on different unit operations | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| TPF-362.4 | Understand the change in product behaviour during different unit operations | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| TPF-362 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| TPF -466 Process Equipment Design | |||||||||||||
| TPF-466.1 | To acquires the knowledge of basics of process equipment design and important parameters of equipment design | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| TPF-466.2 | To identify the appropriate numerical solutions used in equipment design | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| TPF-466.3 | To understand the design procedure of food processing equipments. | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| TPF-466.4 | To develop skill for advances/simulations in design | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| TPF-466 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| TID -221 Irrigation Engineering | |||||||||||||
| TID- 221.1 | Compute the discharge at the head of distributaries required in its command, capacity of a reservoir, evapo-transpiration, irrigation requirement of crop, water requirement of crop, irrigation interval, irrigation period and irrigation efficiencies by applying the knowledge of crop period, crop area, duty, delta and irrigation intensity | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | - |
| TID-221.2 | Analyse the data related to irrigation water measurement through irrigation water measuring structures to estimate the discharge of water measuring structures such as weirs, flumes and notches. | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| TID-221.3 | Design the field channels, Regime Channels, border irrigation, fundamentals of check basin and furrow irrigation. | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | - | 1 |
| TID-221.4 | Solve the real world problem of land grading by calculating the formation levels of grid points of a particular area where land grading operation is to be done | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - |
| TID-221 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| TID -227, Building Material, Construction and Cost estimation | |||||||||||||
| TID-227.1 | Understand; the Building material: stones, lime, cement, Concrete, Sand wood and Timber, Glass, Rubber, Plastics, Metals and alloys Iron | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
| TID -227.2 | Identify; Bricks, Lintels, Arches, Stair case, floors, damp proofing and water proofing, plastering | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| TID-227.3 | Design and construction, Agricultural building sloped and flat roof buildings | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | - | 1 |
| TID-227.4 | Analysis; cost for controlling design, factor affecting building cost, measurement and pricing. | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - |
| TID-227 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| TID -232, Sprinkler and micro irrigation system, 2020-21 | |||||||||||||
| TID -232.1 | Apply: basic understanding of Sprinkler irrigation: adaptability, problems and prospects, types of sprinkler irrigation systems. Micro Irrigation Systems: types-drip, spray, & bubbler systems, merits and demerits, different components. Filter cleaning, flushing & chemical treatment, Fertigation: advantages and limitations of fertigation, fertilizers solubility and their compatibility, precautions for successful fertigation system, fertigation frequency, duration and injection | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| TID -232.2 | Compute: uniformity coefficient and pattern efficiency, wetting patterns, irrigation requirement, emitter selection, hydraulics of drip irrigation system, necessary steps for proper operation of a drip irrigation and sprinkler systems | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| TID-232.3 | Analyse: performance evaluation of sprinkler and drip irrigation systems. necessary steps for proper operation of a drip irrigation system; maintenance of micro irrigation system: clogging problems. selection of pump and power unit for sprinkler and drip irrigation system. | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| TID-232.4 | Design: sprinkler and drip irrigation system: Main, Sub-main, Lateral | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| TID-232 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| TID - 353 Drainage Engineering | |||||||||||||
| TID353-1 | Apply: basic understanding of impact of Water logging objectives of drainage, familiarization with drainage problems of India and state; sub-surface drainage: purpose and benefits, | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| TID353-2 | Compute: different drainage design parameters-hydraulic conductivity, drainable porosity, water table observation wells and piezometers. | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| TID353-3 | Analyse Hooghoudt, Ernst drain spacing equations drainage materials, drainage pipes, drain envelope layout, construction & installation of drains; drainage structures; vertical drainage; bio-drainage; mole drains reclamation of saline & alkaline soils. Cost analysis of surface & sub-surface systems | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| TID353-4 | Design: surface and subsurface drainage systems as well as gravel envelop for different soil and water conditions and conjunctive use of fresh and saline water | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| TID-353 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| TID -362, Ground water wells and pumps 2020-21 | |||||||||||||
| TID362.1 | Study of the Occurrence and movement of ground water and their classification; water lifting devices and their classification. | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TID362.2 | Apply the knowledge of ground water movement and pumps in computation of aquifer parameters and pumping,parameters, respectively. | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TID 362.3 | Analyze well test data for determination of aquifer parameters; and pumping data for Efficiencies, performance, power requirement of different types of pumps | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TID362.4 | Design of wells (open and tube well);different types of pumps (radial pump impeller, volute and diffuser casings) | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TID-362 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| TID-423 ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING | |||||||||||||
| TID-423.1 | Use the techniques for analyzing the meteorology, water supply and sanitation and can apply the knowledge in solving the real time problems of dispersion of pollution, and waste water disposal, treatment and recycling | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | - | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | - |
| TID-423.2 | Compute the ground concentration of air pollutant, water supply and sanitation requirement for a habitat | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | - | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | - |
| TID-423.3 | Analyze the effect of air and water pollution on ecosystem, waste water quantities and methodologies for safe disposal of sewage | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | - | 2 | 3 | 2 | - |
| TID-423.4 | Design the industrial stake, water treatment plants and sewerage system for a habitat | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | - | 3 | 2 | 2 | - |
| TID-423 | |||||||||||||
Common Laboratory & Facilities
| Sr.No. | Name of Laboratories | Area (m2) | Farm Facilities/ Other Instructional Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Language Communication & Skill Development Lab | 90.00 | University Farm, Crop Research Centre, Vegetable Research Centre, Horticulture Research Centre are the other major facilities available centrally for conduct of research and teaching of PG and Ph.d. Students |
| 2. | Central Computing Facility | 1064.00 | |
| 3. | Workshop | 1672.54 | |
| 4. | Hydraulics Lab | 640.00 | |
| 5. | Structure Lab | 298.00 | |
| 6. | Survey Lab | 55.00 | |
| 7. | Refrigeration & Air Conditioning Lab | 152.80 | |
| 8. | Electronics Lab | 153.00 | |
| 9. | Applied Electricity Lab | 63.46 |
List of laboratories
| S.No. | Name of the laboratory | Name of the important equipments |
|---|---|---|
| Farm Machinery and Power Engineering | ||
| Farm Machinery | Various types of ploughs, harrows, seed drills, planters, cultivator, Pneumatic planter, Straw combine, Threshers etc. | |
| Tractor Power | Cut model of tractor, Cut models of two-stroke and four stroke cycle engine, Engine components, clutch gearbox of different type, differential final drive, fuel system, cooling system, lubrication system, electrical system, brake system, steering system etc. | |
| Bio-Energy | Engine test set-up, Gas calorimeter, Gas chromatograph, Gas flow meter and other types of measuring instruments, various types of biogas plant at field laboratory | |
| Animal Mechanics | Universal Testing Machine, Tri-axial test instruments, Animal tread mill, Hardness tester, etc. | |
| Field Practice | Diesel Engines, Various types of tractors | |
| Tillage & Traction | Linear and circular soil test bin | |
| Ergonomics and Human Engineering | Anthropometric Measurement Machine, ergometer etc. | |
| Research Workshop | Lathe machine, Milling machine, Radial drill, Welding set, grinder, Shaper, MIG welding and other instruments used during fabrication work | |
| Soil and Water Conservation Engineering | ||
| Soil & Water Conservation Engg. | Hydraulic tilting flume, Electronic triaxial test apparatus, Electronic direct shear test apparatus, Consolidation apparatus, Automatic compaction machine, Hydraulic tilting flume | |
| Watershed Hydrology & Management | Raingauges, Current meters, Sediment samplers | |
| Computer Lab. | Computers, UPS | |
| Open Lab. | Rainfall simulator, Tilting flume | |
| Irrigation and Drainage Engineering | ||
| Irrigation & Drainage Engg. Lab | Conductivity Meter, Hook Gauge, Soil Resistivity Meter , Oven, Soil Core Sampler , Augurs, Confined well’s model unconfined well’s model, Infiltro meter Parshall Flume, V notch, Weirs | |
| Flow Thorough Porous Media Lab | Vertical Hele-shaw Model, Horizental Hele-shaw Model, Heat Conduction Model, Viscometer, Digital Planimeter, V.T.V.M., Audio Frequency Generator & ACE Signal Tracer | |
| Engineering of Bio System Lab | Anemometer,Soil Moisture meter , Pan Evaparimeter, Lux meter, Soil Moisture Meter, Sun Shine Recorder, Rain Gauge & Remote Sensor With Individual data loggers | |
| Fluid Transport Machinery Lab | Centrifugal Pump setup, Ejecto Pump Setup, Domestic Self Primping Pump, Reciprocating Pump, Hydraulic Ram, Gear Oil Pump Setup, Deep well Bucket Pump Submersible Pump, Cut Model of Centrifugal Pump, Centrifugal Pump Runner, Mixed Flow Pump & Pressure Gauge | |
| Water Quality Testing Lab | Total Organic Carbon Analyzer, Kjeldahl Nitrogen Apparatus, ICS – ION Chromatography System, Multi Parameter Water Quality Instrument, HPLC Model, Soil Analysis Kit Turbidity Meter, TDS Meter | |
| GIS & Remote Sensing Lab | Softwares (Geometica Prime, Mapxtereme, Statistica7.1, Geometica Ortho Engine, Visual Mode Flow Flex, Aquachem, Surfer.11, Didger. 5 and Water Shad Management System) Remote Sensor with Individual loggers, Document Scanner and Differential G.P.S and 11 Computers, UPS etc. | |
| Pump and R & D Lab | Lathe Machine, Arch Welding Machine, Grinder etc. | |
| Computer Simulation Lab | Computers, UPS etc. | |
| Post Harvest Process and Food Engineering | ||
| Down Stream Processing Lab | Vacuum oven, Autoclave, Colony Counter, Water bath, Muffle furnace | |
| Process/PHT lab | BOD Incubator, Fluid Bed Dryer, Vacuum Over | |
| EPBM lab | Carver Press | |
| Quality Control Lab | Ultrasonic Processor Sonicator, Spectrophotometer, Solvent Extraction Unit, Nitrogen Evaporator Unit, Seed/Grain Analyzer, Lab Water purification System | |
| P.G. Computer lab | Computer | |
| Chemical & Glassware Store | Chemical & Glassware | |
| Jagery Lab | - | |
| Storage Lab | Tray Dryer, Hot Air Oven | |
| Development Lab | Welding Machine, Grinding Machine | |
| Rice Milling Lab | - | |
| Food Packaging Lab | - | |
| Wet milling lab | - | |
| Bio conversation | Centrifuge, Rotary Vacuum Evaporator, water activity Meter, Freeze Dryer | |
| Milling Lab | Willy Machine, Dockage, carter day, balance, Hot air oven | |
| R&D Lab | - | |
List of research projects
| S.No. | Deptt. Name | Project Title | Funding Agency | Cumulative Amount for 3 years from 2015-16 | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FMP Engg | AICRP on UAE | ICAR, New Delhi | 127 lacs | Contd | |
| FMP Engg | AICRP on RES | ICAR, New Delhi | Approx 99.63 lacs | Contd. | |
| I&DE | AICRP on Irrigation Water Management | ICAR, New Delhi | 3.5 Crore from 2015 to 2018 | Contd. | |
| Total | Approx. 527 crores | ||||
List of consultancy project
| S.No. | Deptt | Project Title | Funding Agency | Amount earned during last 3 years from 2015-16 | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FMP Engg | Training and testing of Agricultural Implements | RKVY, Uttarakhand | Rs. 25 lacs approx | Contd |
Important Research Achievements The salient achievements of the constituent departments of Agricultural Engineering are as under:
A. Farm Machinery and Power Engineering
| S.No. | Name of equipment/ technology developed |
|---|---|
| Tractor drawn Pantnagar zero-till ferti-seed drill (Commercialized) | |
| Pant- Wheat Thresher for hilly region | |
| Pant spice thresher | |
| Powered Harrow Plough with Seeding attachment | |
| Pant-ICAR Subsoiler-cum-Differential Rate Fertilizer Applicator | |
| Pant winged subsoiler with leading tines | |
| Oscillatory sieve potato digger windrower | |
| IRRI- Pantnagar Multi Crop Axial Flow Thresher | |
| High Capacity Soybean Thresher | |
| Pant spiked clod crusher | |
| Pant adjustable width double neck yoke for hump less animals | |
| Pant adjustable collar harness for single animal | |
| Pant animal drawn zero-till seed drill for hills | |
| Standardization of work-rest cycle for draught animal | |
| Pauri nasuda | |
| Pantnagar Pauri danala | |
| Pantnagar Pauri damala | |
| Paddy thresher-cum-winnower | |
| Hand and foot operated winnower | |
| Gadgets for conversion of diesel engine on biogas-diesel dual fuel | |
| High pressure carbon dioxide scrubber | |
| 6 m3 Pant RCC Biogas plant for high water table areas | |
| 6 M3 completely insulated Pant Tarai Biogas Plant for Cold Regime (1-20 deg C) | |
| Process standardization for bio-diesel production as alternative fuel for CI engine |
B. Soil and Water Conservation Engineering
- Developed a 10 m x 1.2 m rainfall simulation system along with a tilting flume and water circulation system to conduct hydrological studies under lab conditions.
- Developed a portable rainfall simulator to conduct rainfall-runoff sediment studies under field conditions.
- Developed hydrologic models for rainfall-runoff-sediment outflow from natural watersheds of Ramganga River catchment.
- Assessment and monitoring of drought and wet conditions at various places in Uttarakhand State.